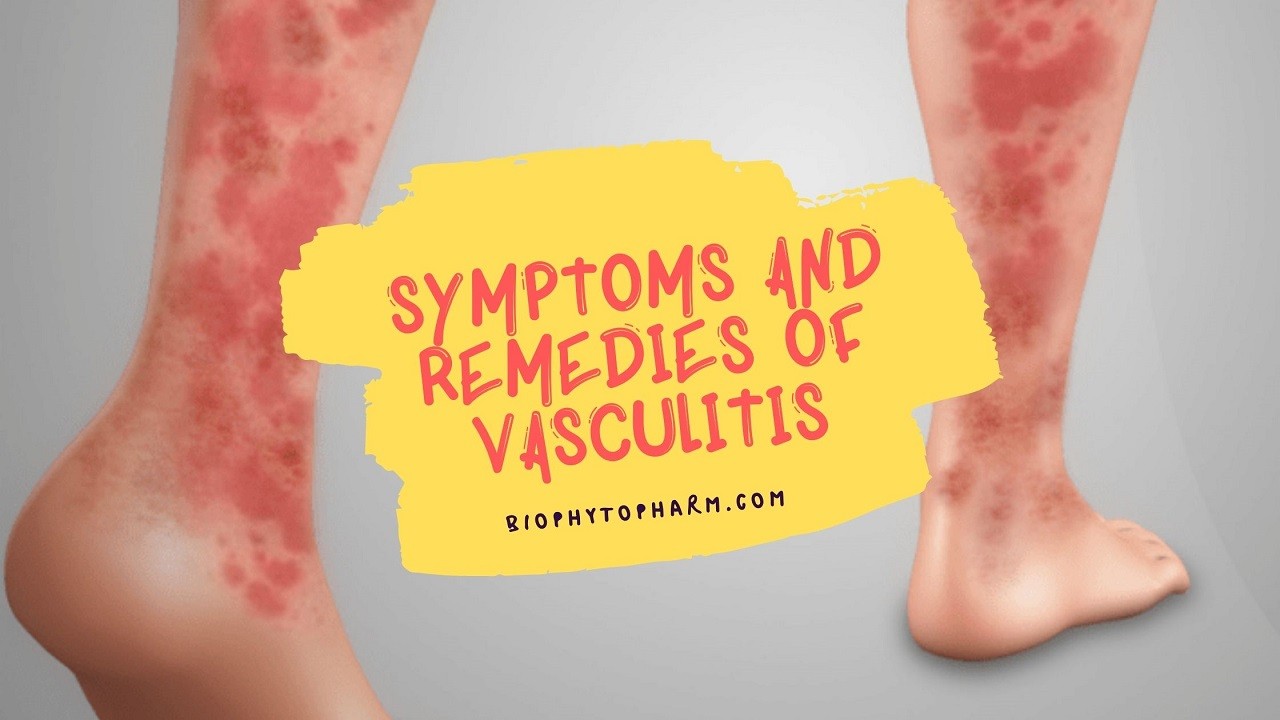
Vasculitis is a medical term used to describe inflammation of the blood vessels. It can be caused by autoimmune diseases, infections, or exposure to certain toxins and medications. Symptoms include pain and tenderness in the area affected, fatigue, joint swelling, skin rashes, fever, and malaise. If left untreated it can lead to organ damage and even death. In this article, we will explore the symptoms and remedies of vasculitis so you can better understand how to treat it.
Vasculitis is a serious condition that should not be taken lightly. Its effects vary depending on the type of disease or infection causing it, but all forms have one thing in common: they cause inflammation of the blood vessels due to an immune system response gone wrong. This inflammatory response causes damage to the walls of your arteries and veins leading to decreased oxygen flow throughout your body which leads to tissue damage.
The good news is that there are treatments available for vasculitis that can help reduce inflammation and minimize long-term damage from occurring. We’ll discuss these treatments as well as what signs you should look out for if you think you may be suffering from this condition to get prompt treatment before more severe complications arise.
Definition
Vasculitis is a medical condition that involves inflammation of the blood vessels. It can affect people of all ages and backgrounds, though it tends to be more common in men than women. This often leads to disruption of normal blood flow, which can cause pain, swelling, and other problems throughout the body.
The symptoms vary depending on what type of vasculitis you have and where it’s located in your body. Common signs include skin rashes, joint pain or stiffness, fever, fatigue, headaches, nausea, chest pain, and shortness of breath. In severe cases, organ damage may also occur due to a lack of oxygenated blood supply.
Treatment for vasculitis typically includes medications such as steroids or immunosuppressive drugs to reduce inflammation and prevent tissue damage. Other therapies such as physical therapy or occupational therapy may also be recommended to help manage discomfort and improve the overall quality of life.
Types Of Vasculitis
Types of Vasculitis include Wegener’s granulomatosis, polyarteritis nodosa, microscopic polyangiitis, and Kawasaki disease. Wegener’s granulomatosis is a type of vasculitis that affects the small blood vessels in the nose, lungs, kidneys, and sinuses. It can cause inflammation in those areas as well as mouth sores and skin rashes. Polyarteritis nodosa is an autoimmune disorder where your body’s immune system attacks its blood vessels. Symptoms may include joint pain, muscle aches, abdominal pain, or tenderness due to organ damage from vessel inflammation. Microscopic polyangiitis is similar to polyarteritis but it typically targets smaller arteries and veins which can result in glomerulonephritis (inflammation of the kidney). Finally, Kawasaki Disease is a rare form of vasculitis that typically affects children under age 5. Its symptoms include fever, rash on arms and legs, swollen lymph nodes in the neck area, and red eyes with crusty eyelids amongst others. Treatment for these types of vasculitides varies depending upon the severity of each case; however, they often involve immunosuppressive medications like steroids or other anti-inflammatory drugs along with lifestyle changes such as quitting smoking if applicable.
Causes Of Vasculitis
Transitioning from the previous section, this article will now discuss the causes of vasculitis. Vasculitis is often caused by an abnormal immune response; when a person’s antibodies mistakenly attack their blood vessels as if they were foreign pathogens. This autoimmune process can be triggered by infection, injury, or certain drugs and chemicals. In some cases, it may also occur without any identifiable cause at all.
Infections are one of the most common triggers for vasculitis. Viral infections such as HIV/AIDS and Hepatitis C have been linked to vasculitis development in some individuals. Bacterial infections like strep throat and tuberculosis can also trigger autoimmunity in rare cases. Additionally, fungal infections including coccidioidomycosis or histoplasmosis may lead to inflammation of small arteries or veins.
Certain medications such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and antibiotics are known to increase a person’s risk of developing vasculitis due to their inflammatory properties. Other environmental factors such as exposure to toxins and radiation could potentially lead to vessel damage resulting in vasculitis symptoms.
Ultimately, many potential causes for vasculitis should be discussed with your doctor so that you can identify the source of your condition and receive appropriate treatment promptly.
Risk Factors For Vasculitis
It’s a worrying thought that our bodies can turn against us and cause physical damage. Vasculitis is one such condition, where the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissues in the blood vessels, causing them to become inflamed and swollen. Understanding what puts us at risk of developing vasculitis is important for reducing this threat.
The most common risk factor associated with vasculitis is age; it tends to affect those aged over 60 more often than any other age group. Additionally, certain medical conditions have been linked to an increased chance of vasculitis:
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Lupus
- Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)
- Sjogren’s syndrome
There are also environmental factors that could be putting you at greater risk of developing vasculitides, such as exposure to certain chemicals or medications. Smoking has also been identified as a possible trigger for some forms of the condition too.
Fortunately, there are measures we can take to reduce our chances of getting this illness. Eating healthily, exercising regularly, and avoiding cigarettes are all great ways to keep your body in top shape and protect yourself from future harm. It may never be completely avoidable but these steps will help give you peace of mind that you are doing everything within your power to stay safe and healthy.
Diagnosing Vasculitis
Diagnosing vasculitis is a complex process, as there are many different types of conditions. A doctor will typically ask about symptoms and medical history before ordering tests to confirm the diagnosis. Diagnostic tests can include blood work, imaging studies like X-rays or ultrasounds, biopsies if necessary, and even genetic testing in some cases.
Blood tests help doctors detect signs of infection, inflammation, or an overactive immune system. Imaging studies such as X-rays and MRIs may be done to look for areas where blood vessels have been damaged by vasculitis. Biopsies are also sometimes taken from affected tissues to examine under a microscope. Genetic testing is available for certain forms of inherited vasculitis that run in families.
Once a diagnosis has been made, treatment options vary depending on the type of vasculitis and its severity. Treatment goals usually involve improving circulation and relieving any pain associated with the condition. Medications such as corticosteroids or immunosuppressants may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and prevent organ damage caused by vasculitis flares up. Surgery may also be recommended for severe cases where medication alone isn’t enough to treat the disease effectively.
Common Indicators And Symptoms
Vasculitis is a disorder that affects the blood vessels and can cause inflammation. Common indicators and symptoms of vasculitis include:
- Painful lumps or rashes on the skin:
- Skin nodules, which are tender bumps that form under the skin
- Reddish-purple spots on the skin (purpura)
- Itching or burning sensations in areas of affected skin.
- Joint pain:
- Swelling in one or more joints due to fluid accumulation (joint effusion).
- Stiffness or difficulty moving certain joints.
- Fatigue: Extreme tiredness; feeling exhausted even after adequate rest.
- Fever: A fever greater than 100°F (38°C), chills, and sweatiness may occur in some cases.
Other possible symptoms include abdominal pain, weight loss, coughing up blood, shortness of breath, numbness or tingling sensation in extremities, visual disturbances such as blurred vision, headaches, and dizziness. Diagnosis typically involves testing for underlying conditions that could be causing these symptoms. Treatment usually includes medications such as corticosteroids and immunosuppressants to reduce inflammation, control pain, and restore the healthy functioning of the body’s organs. In severe cases where medical treatment has not been effective, surgery may be necessary to remove any damaged tissue from the affected area(s). Additionally, lifestyle modifications like quitting smoking and reducing stress levels can help manage symptoms associated with vasculitis.
Complications Associated With Vasculitis
Unfortunately, vasculitis can have various complications if left untreated. These include damage to vital organs, such as the kidneys and heart, which can lead to permanent disability or even death. It is important for individuals affected by this condition to seek medical care to manage their symptoms and reduce any potential complications.
Certain types of vasculitis may also increase an individual’s risk of developing certain cancers. This includes angiocentric lymphoma, a type of cancer that affects the blood vessels inside the body. Additionally, those with autoimmune disorders like lupus or rheumatoid arthritis are at an increased risk of developing vasculitis-related conditions.
Therefore, it is essential for anyone experiencing signs or symptoms associated with vasculitis to consult their doctor immediately so they can be monitored for further progression and receive appropriate treatment. Early diagnosis and management of this condition will help ensure that patients remain healthy and avoid potentially serious health problems caused by vasculitis.
Medication And Treatment Options
Medication and treatment options for vasculitis vary depending on the type, severity, and location of the condition. In general, corticosteroids are often used to reduce inflammation in affected blood vessels. Immunosuppressive medications may also be prescribed to suppress or modulate an overactive immune system response. Depending on the individual’s symptoms and diagnosis, additional treatments such as antimalarial drugs, biological therapies, plasmapheresis (the removal of plasma from the bloodstream), chemotherapy, antibiotics, pain relievers, and physical therapy may also be recommended.
In some cases where lifestyle changes cannot effectively manage symptoms of vasculitis, surgery might be required. Surgery can involve removing damaged sections of a vessel, bypassing them with healthy tissue or a graft from another part of the body, or stopping blood flow completely to certain areas by inserting vascular plugs. With these procedures comes a risk for infection so doctors typically recommend that patients take preventive measures before undergoing any invasive procedure.
Treatment plans should always be discussed with a physician who is knowledgeable about your specific condition and its potential complications. The aim is to treat underlying causes while managing associated pain and other symptoms. Each patient responds differently to different treatments so it is important to find what works best for you under medical supervision.
Corticosteroids
Corticosteroids are one of the most effective forms of treatment for vasculitis. For example, a 12-year-old girl with Wegener’s Granulomatosis was treated successfully with corticosteroid therapy. The goal of this type of therapy is to reduce inflammation and suppress the immune system. Corticosteroids can be taken orally or intravenously, depending on the severity of the symptoms. They have been known to work quickly in reducing swelling, fever, and joint pain associated with vasculitis.
In addition to managing these active symptoms, oral doses of corticosteroids may also help prevent further damage from occurring by controlling flare-ups. It is important to take them as prescribed because abruptly stopping use can lead to a relapse due to an increase in inflammation again; this could cause more permanent tissue damage if left untreated. So it’s best to keep taking them until instructed otherwise by your doctor.
While corticosteroids are effective at treating many types of vasculitis, they do come with some potential side effects such as weight gain, increased risk for infection, nausea/vomiting, and mood swings. Some people might experience serious complications like Cushing syndrome which causes weakening bones and thinning skin amongst other issues so you must talk to your doctor about any concerns you may have before starting treatment. Taking control of your health is essential when dealing with a condition like vasculitis as early management can be key in controlling your long-term prognosis!
Immunosuppressive Drugs
Moving on from corticosteroids, immunosuppressive drugs are often used to treat vasculitis. These medications work by suppressing the immune system, thereby preventing it from attacking healthy tissues and organs. Immunosuppressants can be very effective at reducing inflammation in people with vasculitis, but they also come with a risk of side effects such as increased susceptibility to infections.
Common immunosuppressive medications prescribed for treating vasculitis include cyclophosphamide (Cytoxan) and azathioprine (Imuran). Cyclophosphamide is usually given intravenously or orally over several weeks or months, while azathioprine is taken daily in pill form. Both medications have been found to reduce inflammation and improve symptoms in some patients with vasculitis.
Other treatments may also be needed depending on the type of vasculitis a person has and how far it has progressed. In addition to medications, lifestyle changes like getting plenty of rest and avoiding smoking can help manage the disease and reduce flare-ups. It’s important to speak with your doctor about the best course of treatment for you.
Biological Agents
It is estimated that up to 10% of all cases of vasculitis are caused by biological agents. These agents can include bacteria, fungi, and viruses, as well as environmental toxins or drugs. In this section, we will discuss the symptoms and remedies associated with these types of agents.
Common signs and symptoms of a viral infection that may cause vasculitis to include:
- Fever
- Swelling in joints
- Fatigue
- Skin rashes
Treating bacterial or fungal infections involves antibiotics, antifungal medications, or other medications depending on the type of agent causing the infection. For viral infections, antiviral medications such as acyclovir or valacyclovir can be prescribed for reducing inflammation in blood vessels. Additionally, corticosteroids may also be used to reduce inflammation and help improve overall health. However, it’s important to note that corticosteroids should not be used long-term due to their potential side effects. Finally, lifestyle modifications such as avoiding smoking and alcohol consumption are recommended for helping manage symptoms related to vasculitis caused by biological agents.
Surgery
Moving on from biological agents, surgery may be recommended for more severe cases of vasculitis. Surgery is usually the last resort and should only be considered when other treatments have failed to provide relief or show any signs of improvement. Generally speaking, surgical procedures aim to remove or repair damaged blood vessels that are causing symptoms such as pain or swelling.
The most common types of surgeries used in treating vasculitis include angioplasty, stent placement, thrombolysis, bypass grafting, and endarterectomy. Angioplasty involves using a catheter to open narrowed arteries by inflating a balloon inside them; this restores normal circulation and helps reduce pain. Stenting involves placing metal tubes called ‘stents’ in an artery that has been narrowed due to plaque buildup; this help keeps the artery open and restores the normal flow of blood. Thrombolysis involves injecting drugs into an affected artery to dissolve clots and improve circulation; however, it can carry some risks so it must be done with caution. Bypass grafting is another option where surgeons create new pathways around blocked areas to ensure proper circulation throughout the body These techniques are all effective ways of managing the symptoms associated with vasculitis but they come with their own set of risks including infection, bleeding, stroke, and even death in rare cases.
Surgery often provides long-term relief for those affected by vascular inflammation but there are also several lifestyle changes one can make to ease discomfort caused by vasculitis. Eating a healthy diet rich in fruits and vegetables while avoiding processed foods could help decrease inflammation levels within the body as well as quitting smoking if you smoke currently which will further reduce risk factors associated with developing vasculitis itself. Additionally getting regular exercise (under a doctor’s guidance) helps maintain good health overall which can significantly lessen effects related to certain forms of vascular inflammation.
Natural Treatments, Essential Oils, And Home Remedies
It is theorized that natural treatments, such as essential oils and home remedies can be effective in treating vasculitis. Here are 5 ways to start improving your condition:
- Drink more fluids to stay hydrated
- Take a daily multivitamin to ensure adequate nutrient intake
- Add anti-inflammatory foods, like turmeric and ginger, into your diet
- Consider trying aromatherapy with specific essential oils like lavender or chamomile
- Get plenty of rest when possible
Apart from these home remedies, there is also evidence that some supplements may help manage the symptoms related to vasculitis. A study found that omega-3 fatty acids could improve inflammation levels associated with the disease. Additionally, Vitamin B12 has been linked to aiding in reducing fatigue caused by the illness. It’s important to consult a healthcare professional before taking any supplement, however.
Finally, it’s vital for those suffering from vasculitis that they exercise regularly and get regular checkups with their doctor so they can monitor their progress and make necessary adjustments for improved health outcomes.
Coping With Vasculitis
Coping with vasculitis can be a challenging experience. It’s important to understand that vasculitis is an unpredictable disease, and its symptoms may come and go throughout treatment. Taking care of yourself is paramount in living with this condition. Here are some tips for coping with vasculitis:
First off, get informed about your condition. Talk to your doctor or healthcare provider about any concerns you have, including potential triggers and lifestyle changes necessary to manage them effectively. Educating yourself on the signs and symptoms of flare-ups will help you better recognize them when they occur. You should also discuss the long-term outlook for your type of vasculitis so that you can plan accordingly.
In addition, take steps to reduce stress levels associated with living with a chronic illness such as vasculitis. Relaxation techniques like yoga or meditation can help manage anxiety related to having a potentially life-threatening disease. Additionally, make sure you have emotional support from family and friends who understand what you’re going through and provide encouragement during difficult times.
Finally, follow your prescribed treatment regimen closely; don’t skip doses or self-medicate without consulting your doctor first. Pay attention to any warning signs that could indicate another flare-up and report these promptly to your physician right away so adjustments can be made if necessary. Living well with this autoimmune disorder requires dedication but proper management can result in improved quality of life over time.
Impact On Long-Term Health
The impact of vasculitis on an individual’s long-term health can be devastating. It is a silent enemy that slowly creeps up and destroys the body before one has time to react. Every organ system in the human body has the potential to suffer serious damage if left untreated, which makes early diagnosis critical for successful treatment and recovery.
First and foremost, any kind of inflammation or infection can affect the heart and its functioning. Vasculitis increases risk factors such as high cholesterol levels, hypertension, and diabetes – all of which contribute to cardiovascular issues like stroke or even heart failure. In addition, individuals with vasculitis may develop kidney problems due to a lack of blood supply supplied to this vital organ. This often results in renal failure requiring dialysis treatments or even transplantation.
Finally, other organs may also experience adverse effects such as respiratory difficulties caused by lung involvement; joint pain due to arthritis; skin complications like ulcers; neurological deficits resulting from nerve damage; eye issues because of retinal inflammation; gastrointestinal distress leading to abdominal discomfort, diarrhea, constipation, etc.; hearing loss associated with ear infections; fatigue because of extreme exhaustion from chronic illness; psychological struggles related to depression and anxiety due to constant suffering…the list goes on. All these ailments combined make living with vasculitis incredibly challenging and life-altering for those affected – sometimes leading them down a pathway where there seems no return back!
Frequently Asked Questions
What Lifestyle Changes Can I Make To Help Prevent Vasculitis?
Vasculitis is an inflammation of the blood vessels which can be potentially serious, so it’s important to take steps to prevent it. Fortunately, there are a few lifestyle changes you can make that may help reduce your risk.
Firstly, maintaining a healthy weight is key to reducing your chances of developing vasculitis. Eating a balanced diet and exercising regularly can go a long way in preventing this condition:
- Exercise: Aim for 30 minutes or more of moderate-intensity exercise five days per week; such as walking, swimming, and cycling.
- Diet: Eat plenty of fruits and vegetables, lean meats, low-fat dairy products, whole grains, nuts, and seeds. Avoid processed foods high in sugar and fat.
- Supplements: Taking omega-3 fatty acids may reduce inflammation levels linked with vasculitis symptoms.
Secondly, if you smoke then quitting will lower your risk significantly since smoking reduces blood vessel elasticity which can lead to vasculitis flares. If you’re having trouble quitting on your own, consider joining a support group or asking for advice from your doctor about medications that might help you quit successfully.
Finally, managing stress could also play an important role in prevention as chronic stress has been linked with increased inflammation throughout the body – including the blood vessels involved in vasculitis flare-ups. Try calming activities like yoga or tai chi and practice mindful meditation techniques when feeling overwhelmed by anxiety or worry.
Are There Any Dietary Restrictions Associated With Vasculitis?
Dietary restrictions are an important part of managing vasculitis. While there is no one-size-fits-all approach to diet for people with this condition, certain foods and drinks may need to be avoided or limited in order to reduce inflammation, promote healing, and help prevent flare-ups. Here are some tips on how you can make dietary changes that will benefit your overall health:
- Increase consumption of omega-3 fatty acids such as salmon, sardines, flaxseed oil, and walnuts.
- Reduce processed carbohydrates by limiting white bread, pastries, cookies, crackers, and other refined grains.
- Avoid sugary beverages like soda and juice as much as possible.
- Eat more fresh fruits and vegetables which are high in fiber and antioxidants.
- Choose lean proteins such as fish, poultry, beans, and legumes instead of red meat.
Making these changes can be difficult at first but the benefits outweigh any temporary inconvenience. Eating a balanced diet with plenty of natural whole foods helps support the body’s ability to heal itself from conditions like vasculitis. Additionally, it is important to keep hydrated throughout the day by drinking plenty of water and avoiding caffeine or alcohol which can cause dehydration.
It’s also beneficial to consult a nutritionist who specializes in autoimmune diseases when making dietary changes so they can provide personalized guidance tailored to your specific needs. They can help you create meal plans that meet your nutritional requirements while staying within your budget. With their assistance, you can find ways to stick with healthy eating habits even during busy times or when dining out at restaurants.
Ultimately it’s necessary for those living with vasculitis to pay attention to what food choices they make each day in order to maintain good health and avoid complications from this serious medical condition. Making small adjustments over time can have a big impact on both short-term relief from symptoms as well as long-term prevention against flare-ups down the road
How Long Do I Need To Take Medications And Treatments For Vasculitis?
How long do I need to take medications and treatments for vasculitis? This is a difficult question to answer without knowing the specific details of an individual’s case. The length of time required can vary depending on several factors, such as the severity of the condition, how quickly it responds to treatment, and any underlying health conditions the person may have.
In general, most people with vasculitis will require long-term medication or therapy in order to manage their symptoms and reduce further damage to their blood vessels. This may include corticosteroids which help reduce inflammation; immunosuppressants, which are used to control your body’s immune response; or biologic agents, which block certain proteins that cause inflammation. These drugs may be taken orally or injected directly into the bloodstream. Additionally, lifestyle changes such as quitting smoking, exercising regularly and eating a healthy diet can help improve overall outcomes from vasculitis treatment.
The amount of time you’ll need to stay on these medications and therapies depends on your individual needs and should be discussed with your healthcare provider. Your doctor should also provide follow-up care throughout this period so they can adjust dosages if needed and monitor any potential side effects from the treatment plan. It’s important that you keep up with all recommended appointments so that your medical team can ensure you’re receiving optimal care for your condition.
What Are The Chances Of The Vasculitis Returning After Treatment?
The chances of vasculitis returning after treatment can be a frightening thought. While it is impossible to guarantee that the condition will not return, there are ways to reduce this likelihood and stay healthy. Like most medical conditions, early detection and prompt treatment provide the best chance for successful outcomes.
When considering recurrence rates of vasculitis, many factors must be taken into account. The type of vasculitis being treated, as well as how aggressive the disease was before treatment began, often determine whether or not the condition may return. In addition, lifestyle choices such as diet and exercise play an important role in reducing the risk of relapse. Furthermore, following up with regular checkups helps detect any abnormalities or changes that could indicate a potential flare-up before symptoms become severe.
Taking all these considerations seriously is key to minimizing the chances of suffering from a recurrent episode of vasculitis. With proper monitoring and proactive care through lifestyle adjustments and follow-up visits, people diagnosed with vasculitis can manage their health effects over time. Allowing them to lead full lives without having to worry about frequent relapses or long-term complications arising from untreated episodes.
Are There Any Support Groups Available For People With Vasculitis?
For people who have been diagnosed with vasculitis, support groups can provide a much-needed source of comfort and understanding. These groups allow patients to connect with others who are going through the same experience, providing an opportunity for sharing experiences, treatments, and coping strategies. Moreover, they can offer valuable advice regarding dealing with medical appointments, managing medication side effects, and other practical matters.
In general, support group members will be able to empathize with one another in ways that family or friends may not be able to do. They understand what it feels like to live with this condition day-to-day and how challenging it can be at times. Additionally, many participants find strength from knowing that they’re not alone on their journey; rather there is a community of individuals willing to lend emotional support when needed.
Finding a suitable online or offline support group is often as simple as doing some research to locate local chapters or organizations that cater specifically to those living with vasculitis. Some national associations provide information about regional branches which hold regular meetings for members along with resources such as newsletters or educational materials about the disease. Alternatively, social media platforms also offer virtual communities where users can engage in meaningful conversations and receive help from each other in real-time.
Conclusion
We have discussed the symptoms and remedies of vasculitis. Living with this condition can be challenging, but it doesn’t have to determine your life. Making lifestyle changes such as eating a healthy diet and avoiding smoking can help reduce flare-ups and improve your quality of life. Medications, treatments, and support groups are also available to provide relief from the effects of vasculitis.
No one should feel alone in dealing with this illness. There is always someone there to listen and offer advice or comfort when needed. With proper care and management, you can still live an active and fulfilling life even after being diagnosed with vasculitis.